The data indicate that an aberrantly active IL23/IL17 axis contributes to the development of nephritis in lupusprone mice Lupus nephritis affects more than 50% of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) 4 and is a major cause of morbidity ( 1 )IL23/IL17 axis in ankylosing spondylitis VC 15 British Society for Immunology, Clinical and Experimental Immunology, 1 30–36 31 Veldhoen et al suggested later that IL23 probably acts upon previously differentiated Th17 cells to induce amplifiThe discovery IL23IL17 immune axis has thus brought about fundamental changes in cellular immunology and more importantly improved the quality of life for many patients Acknowledgments COI SLG has received a research grant from Novartis;
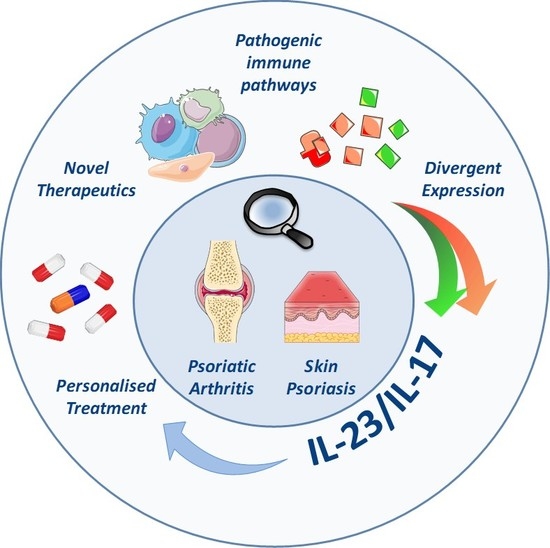
Ijms Free Full Text Role Of The Il 23 Il 17 Axis In Psoriasis And Psoriatic Arthritis The Clinical Importance Of Its Divergence In Skin And Joints Html
The il-17/il-23 axis of inflammation in cancer friend or foe
The il-17/il-23 axis of inflammation in cancer friend or foe-Interleukin23 (IL23) is a heterodimeric cytokine composed of an IL12B subunit (that is shared with IL12) and the IL23A subunit IL23 is part of IL12 family of cytokines A functional receptor for IL23 (the IL23 receptor) has been identified and is composed of IL12R β1 and IL23R Adnectin2 is binding to IL23 and compete with IL23/IL23R mRNA of IL23R is 2,8 kB in length andRole of the IL23/IL17 Axis in Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis The Clinical Importance of Its Divergence in Skin and Joints by MarieAstrid Boutet 1, Alessandra Nerviani 1, Gabriele Gallo Afflitto 2 and Costantino Pitzalis 1,* 1
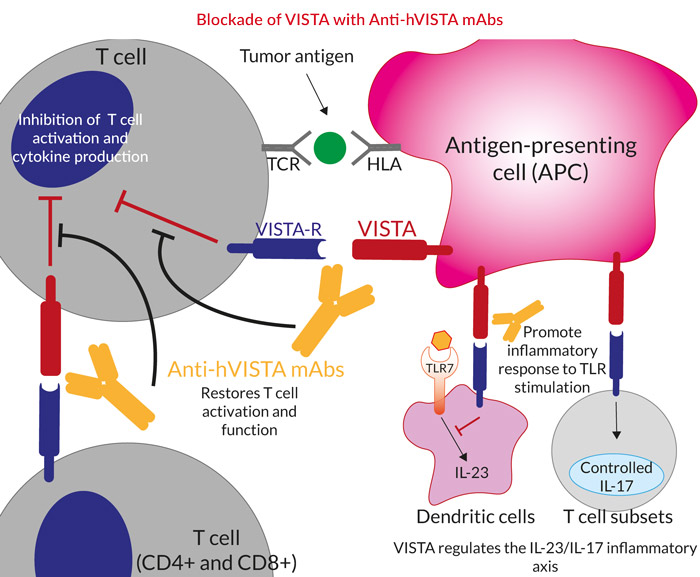


Anti Hvista Mabs Igg1 Isotype Family Invivogen
Psoriasis has been primarily considered a Th1mediated disease, today it is known that the IL23/IL17 axis governs the accelerated progress of inflammation 84,85 Briefly, IL17 attracts neutrophils to the epidermis of psoriatic skin lesions through neutrophil chemoattractants and recruits additional dendritic cells via upregulation of CCLRecent studies indicate a central role for the IL23/IL17 axis in the pathogenesis of lupus nephritis (LN) but the importance in the context of treatment outcome is unknown We studied various cytokines, including the IL23/IL17 axis, in association to histopathology and response to therapy Fiftytwo patients with active LN were includedThis systematic review and meta‐analysis evaluated the efficacy and safety of induction therapy (12–16 weeks) with biologic therapies targeting the IL‐23/IL‐17 immune axis for the treatment of moderate‐to‐severe plaque psoriasis Twenty‐seven randomized controlled trials met the specified inclusion criteria
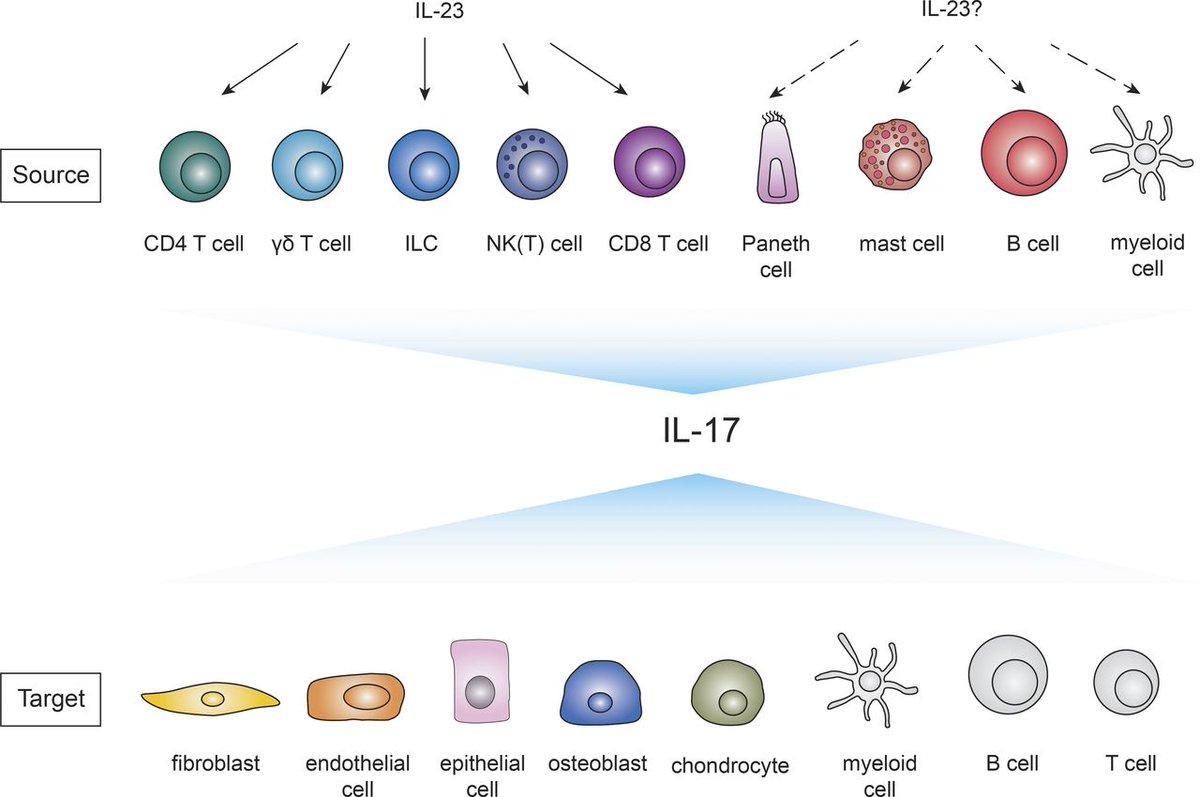
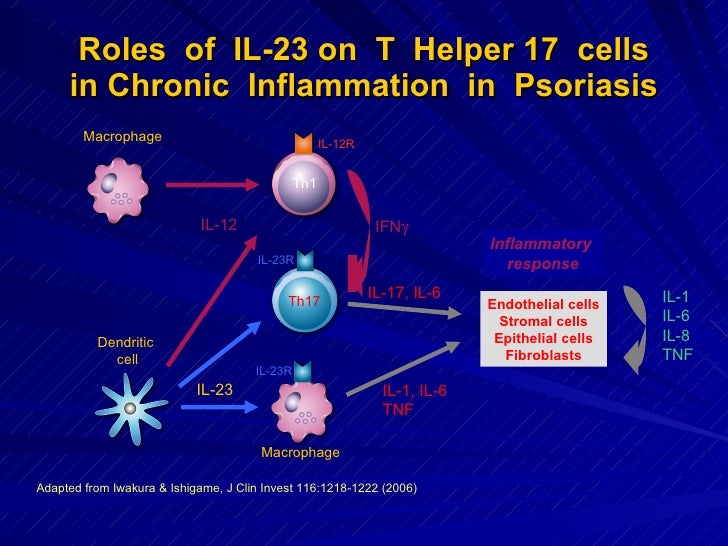
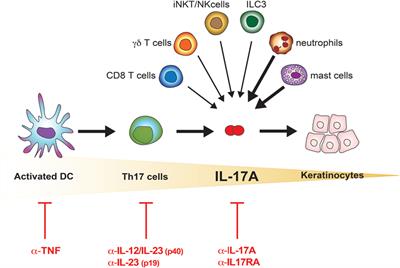
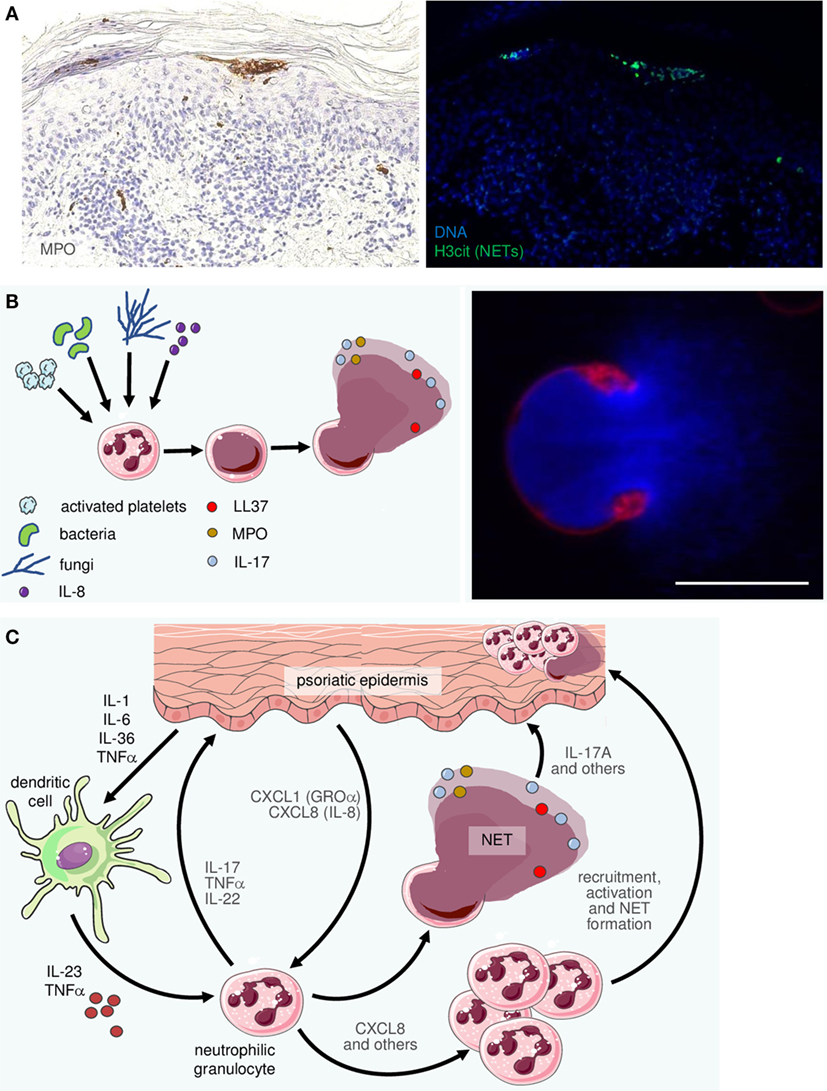
The IL23/IL17 axis clearly illustrates the close interaction of different components of the innate immune system (in this case IL23producing myeloid cells, granulocytes, macrophages, and mast cells) with cells of the adaptive immune system (Th17 and IL17producing CD8 T cells) in psoriasisThe IL23/IL17 axis has a pivotal role in the complex pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel diseases, which lead to the development of several therapeutics targeting different components within this pathway Targeting IL12/IL23p40, as well as IL23p19, seems efficacious and safe in the treatment of moderatetosevere Crohn's disease in recentIcal review discusses the IL23/IL17 axis and the role of T regulatory cells (Treg)/Th17 cells in RA and joint destruction Discussion Role of the IL23p19/IL17 axis in RA IL23p19 and IL17 correspond to a new axis that drives immune activation and chronic inflammation through the differentiation and activation of Th17 cells Both IL17 and
IL23/IL17 axis in ankylosing spondylitis VC 15 British Society for Immunology, Clinical and Experimental Immunology, 1 30–36 31 Veldhoen et al suggested later that IL23 probably acts upon previously differentiated Th17 cells to induce amplifiThe IL23–IL17 axis is critically involved in the development of autoimmunity Tissuespecific IL17A expression exacerbates tissue damage and disease chronicity The roles of IL23 and IL17 atPsoriasis has been primarily considered a Th1mediated disease, today it is known that the IL23/IL17 axis governs the accelerated progress of inflammation 84,85 Briefly, IL17 attracts neutrophils to the epidermis of psoriatic skin lesions through neutrophil chemoattractants and recruits additional dendritic cells via upregulation of CCL



Full Text Current Perspective On The Role Of The Interleukin 23 Interleukin 17 A Itt



The Il 23 T17 Pathogenic Axis In Psoriasis Is Amplified By Keratinocyte Responses Trends In Immunology
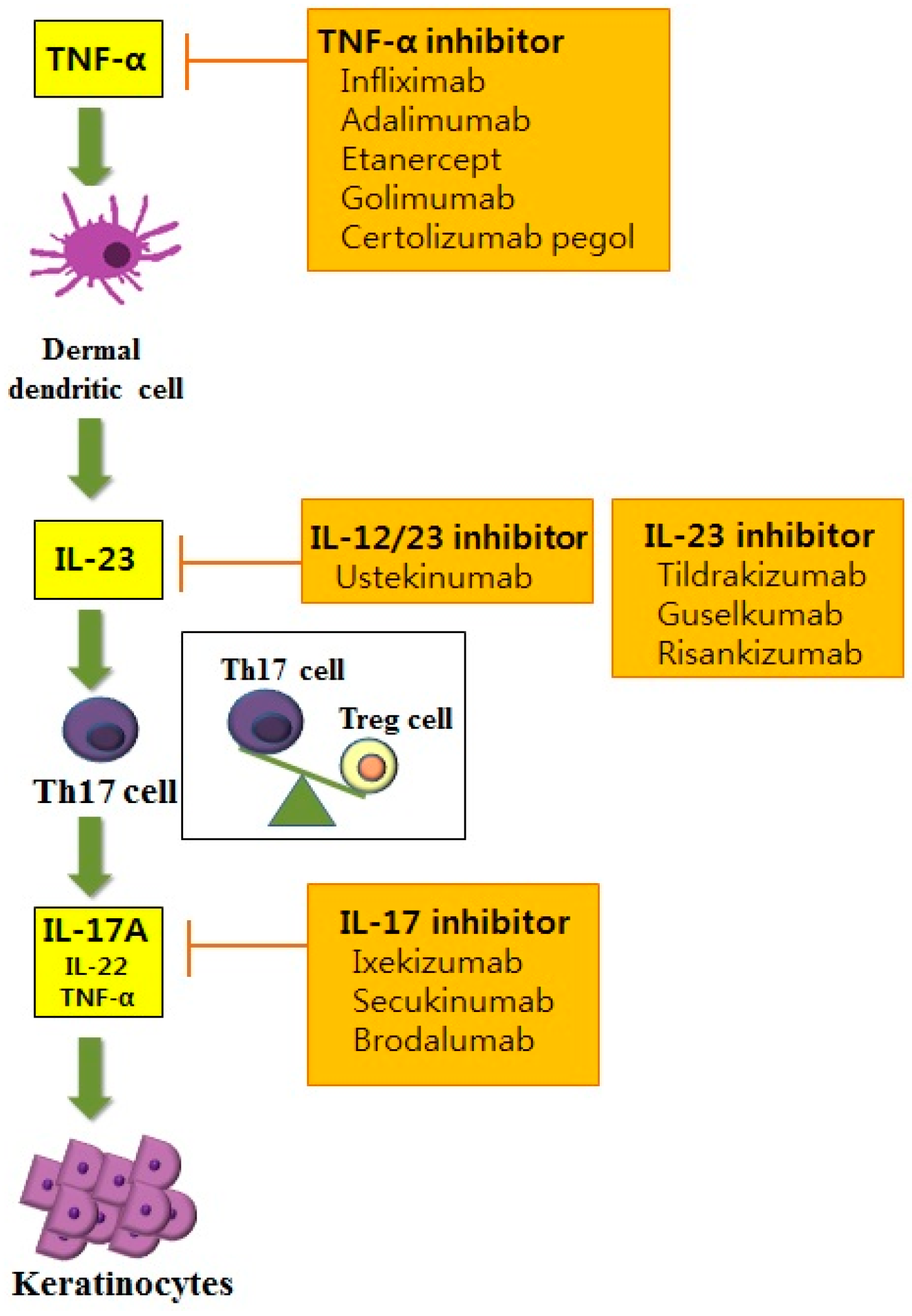
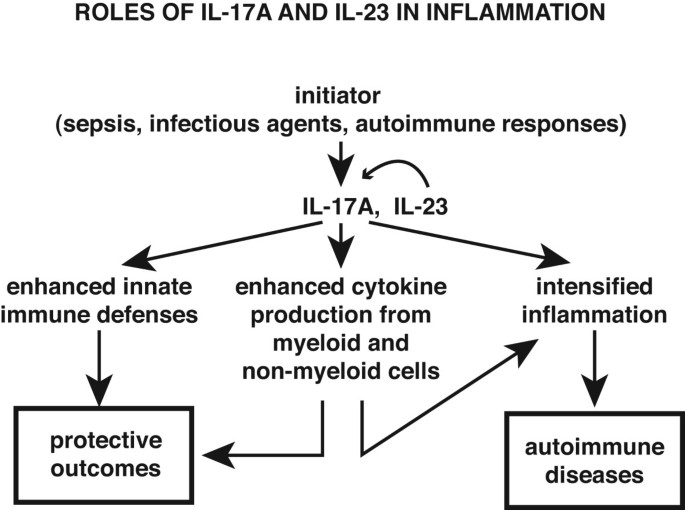
IL23/IL17 axis cytokines are important players in the pathogenesis of psoriasis and PsA Inhibition of IL23 and IL17 with MoAbs is a very effective therapy for both psoriasis and PsA The numbers of these agents are increasingThe IL23/IL17 axis clearly illustrates the close interaction of different components of the innate immune system (in this case IL23producing myeloid cells, granulocytes, macrophages, and mast cells) with cells of the adaptive immune system (Th17 and IL17producing CD8 T cells) in psoriasisThe IL23/IL17, but not IL12/IFNγ, axis is critical for the development of autoimmune inflammatory diseases The development of autoimmune diseases, such as RA, MS, and –/–IBD, is thought to be mediated by Th1 cells because high levels of IL12 and IFNγ are detected in inflam



Il 17 And Therapeutic Kynurenines In Pathogenic Inflammation To Fungi The Journal Of Immunology



The Il 23 Th17 Axis In The Immunopathogenesis Of Psoriasis Sciencedirect
Cytokines members of the IL23/IL17 family, critical in the development of autoimmunity, are abundantly expressed within the cutaneous lesions but also seem to be involved in chronic inflammation and damage of the synovium though, as it will be here discussed, not in all patientsThe role of the IL23/IL17 axis in inflammation and infection The IL23/IL17 axis plays an important role in the development of chronic inflammation and in host defenses against bacterial infectionThe important function of TH 17 cells and its related IL23/IL17 axis in psoriasis is now well accepted and studied 4 In our study, we found a significant correlation between the tissue



Discovery Of The Il 23 Il 17 Signaling Pathway And The Treatment Of Psoriasis The Journal Of Immunology



Il 36 Signaling Facilitates Activation Of The Nlrp3 Inflammasome And Il 23 Il 17 Axis In Renal Inflammation And Fibrosis American Society Of Nephrology
The IL23/IL17 axis plays a critical pathogenic role for both PsA and Ps, and biologics neutralizing IL17A or IL23/IL12 are effective therapies for PsA and Ps The differential expression of Th17 cytokines IL17 and IL22 at various sites could explain the different manifestations of the diseaseThe role of IL23/IL17 axis in lupus nephritis Zhang Z(1), Kyttaris VC, Tsokos GC Author information (1)Division of Rheumatology, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA , USA T cells that express IL17 infiltrate the kidneys of patients with systemic lupus erythematosusFunctional Relevance of the IL23–IL17 Axis in Lungs In Vivo Stefan Ivanov, Steven Bozinovski, Apostolos Bossios, Hadi Valadi, Ross Vlahos, Carina Malmha¨ll, ¨ strand, Jay K Kolls, Gary P Anderson, and Anders Linde´n Margareta Sjo Lung Pharmacology and Immunology Groups, Department of Internal Medicine/Respiratory Medicine and Allergology, Institute of Medicine, Sahlgrenska Academy at



Il 36 Signaling Facilitates Activation Of The Nlrp3 Inflammasome And Il 23 Il 17 Axis In Renal Inflammation And Fibrosis American Society Of Nephrology


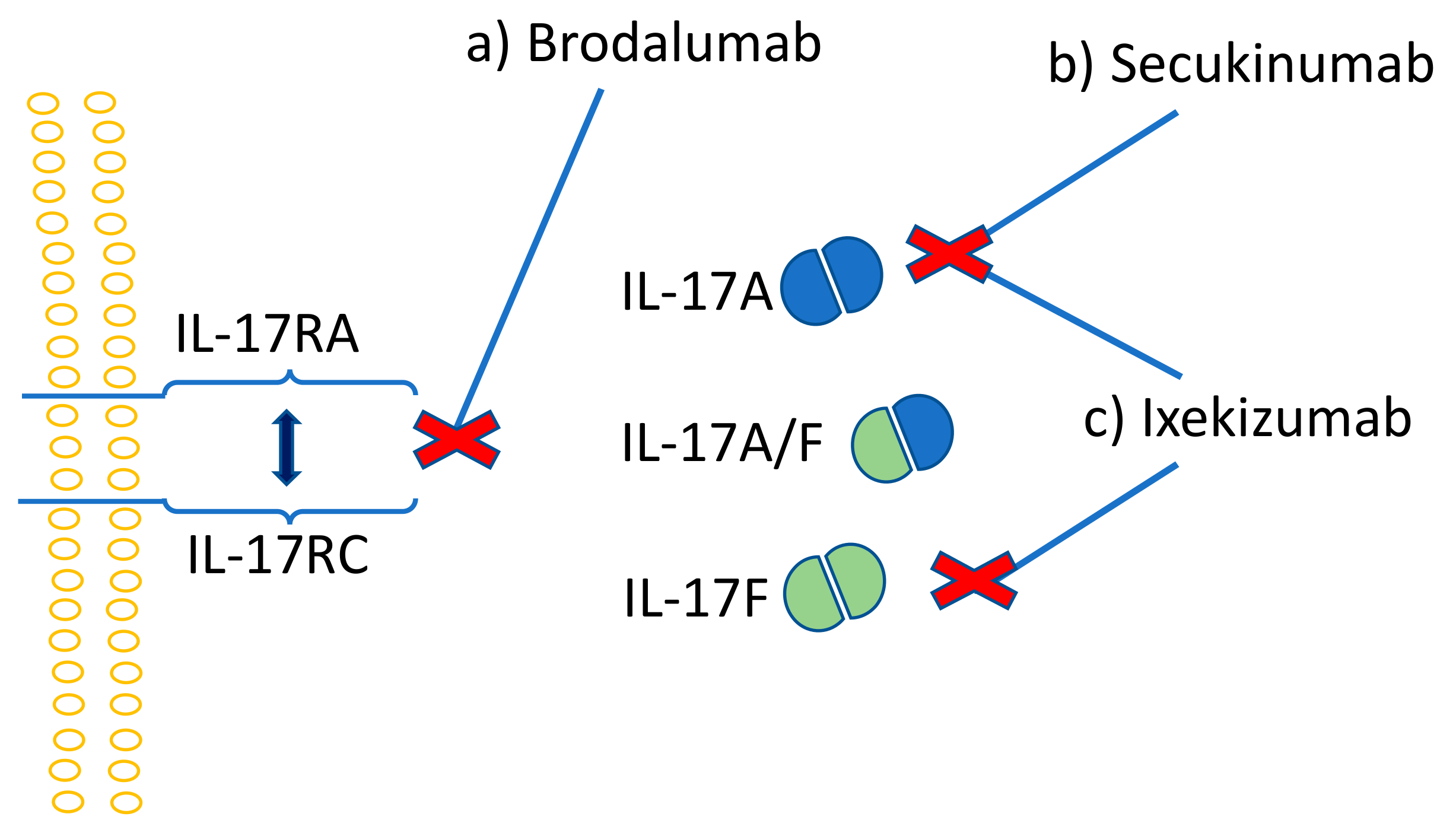
Brodalumab For Psoriasis What A Mess Sugarcone Biotech
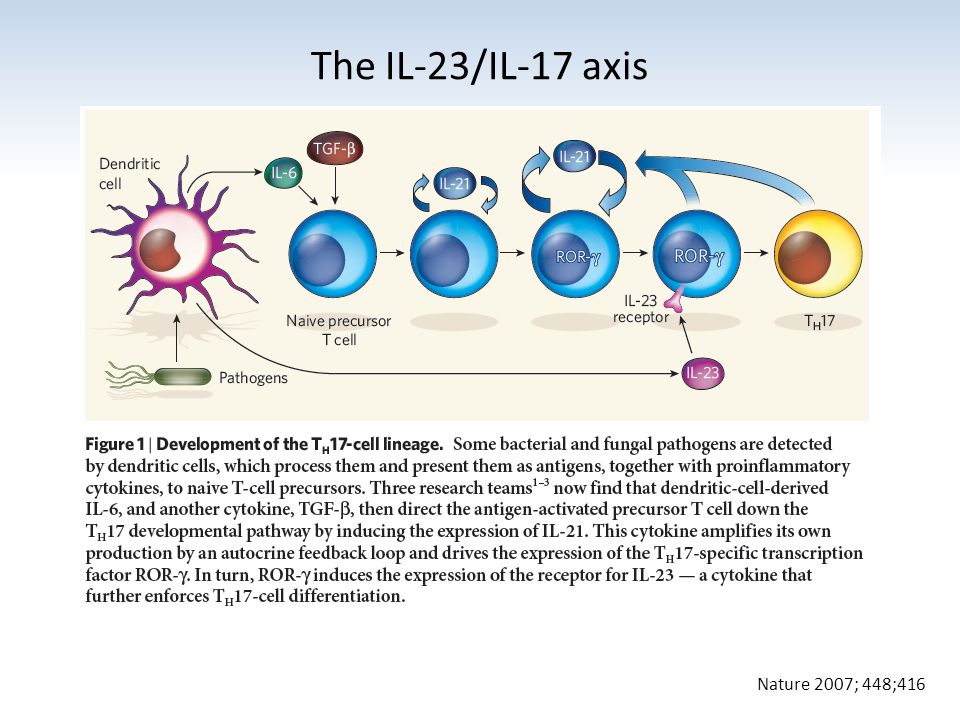
The IL23/IL17, but not IL12/IFNγ, axis is critical for the development of autoimmune inflammatory diseases The development of autoimmune diseases, such as RA, MS, and IBD, is thought to be mediated by Th1 cells because high levels of IL12 and IFNγ are detected in inflammatory sites ( 9 )However, the interleukin 23 (IL‐23)/T‐helper 17 (T H 17) immune axis has been identified as a major immune pathway in psoriasis disease pathogenesis Central to this pathway is the cytokine IL‐23, a heterodimer composed of a p40 subunit also found in IL‐12 and a p19 subunit exclusive to IL‐23In addition, an intact IL23IL17 axis seems to be essential for host protection against Citrobacter rodentium, as well as in the pathogenesis of certain autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (17, 22, 24, 25)



Anti Hvista Mabs Igg1 Isotype Family Invivogen



Interleukin 17 And Type 17 Helper T Cells Nejm
The IL23/IL17 axis plays a critical role in osteoclastogenesis via a number of direct and indirect effects that both positively and negatively modulate osteoclast formation Evidence that IL23 negatively regulates osteoclastogenesis comes from in vitro observations indicating indirect inhibition via T cells ,The IL‑23–IL‑17 axis is critically involved in the development of autoimmunity Tissue‑specific IL‑17A expression exacerbates tissue damage and disease chronicityInterleukin23 (IL23) is a heterodimeric cytokine composed of an IL12B subunit (that is shared with IL12) and the IL23A subunit IL23 is part of IL12 family of cytokines A functional receptor for IL23 (the IL23 receptor) has been identified and is composed of IL12R β1 and IL23R Adnectin2 is binding to IL23 and compete with IL23/IL23R mRNA of IL23R is 2,8 kB in length and



The Interleukin Il 23 Il 17 Axis In Ankylosing Spondylitis New Advances And Potentials For Treatment Jethwa 16 Clinical Amp Experimental Immunology Wiley Online Library
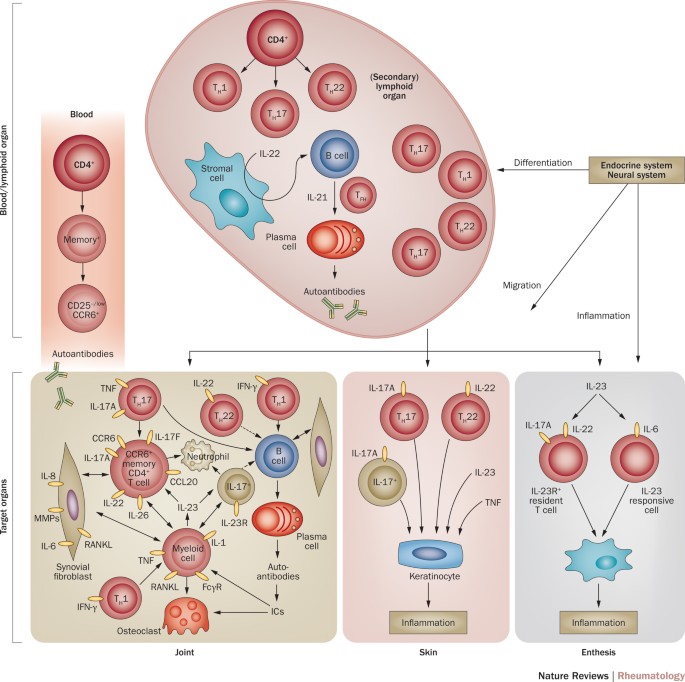


The Il 23 Il 17 Axis In Inflammatory Arthritis Nature Reviews Rheumatology
The role of IL‐23/IL‐17 axis in human kidney allograft rejection Youssra Haouami Research Laboratory in Immunology of Renal Transplantation and Immunopathology (LR03SP01), Charles Nicolle Hospital, Tunis El Manar University, Tunis, Tunisia Search for more papers by this authorThe chronic skin inflammation psoriasis is crucially dependent on the IL23/IL17 cytokine axis Although IL23 is expressed by psoriatic keratinocytes and immune cells, only the immune cellRheumatoid arthritis (RA) and spondyloarthritis (SpA) are the two most common forms of chronic immunemediated inflammatory arthritis, and the IL23IL17 axis is thought to have a critical role in both



Figure 1 From Pathogenic Role Of Il 17 In Psoriasis And Psoriatic Arthritis Semantic Scholar



Interleukin 23 In Psoriasis Integrating New Therapies In The Current Treatment Landscape European Medical Journal
Psoriasis has been primarily considered a Th1mediated disease, today it is known that the IL23/IL17 axis governs the accelerated progress of inflammation 84,85 Briefly, IL17 attracts neutrophils to the epidermis of psoriatic skin lesions through neutrophil chemoattractants and recruits additional dendritic cells via upregulation of CCLThese studies suggest that the IL23/IL17 pathway may be a novel therapeutic target for the treatment of chronic inflammatory diseasesCytokines in the IL23/IL17 axis are not functionally interchangeable due to complex biology and feedback mechanisms This is illustrated for IL17 and IL23 by the discovery of IL23independent IL17 production ( Lee et al, 15 , Schon and Erpenbeck, 18 ) and by the nonequivalence of IL23 and IL17 inhibitors in the clinic ( Furue et
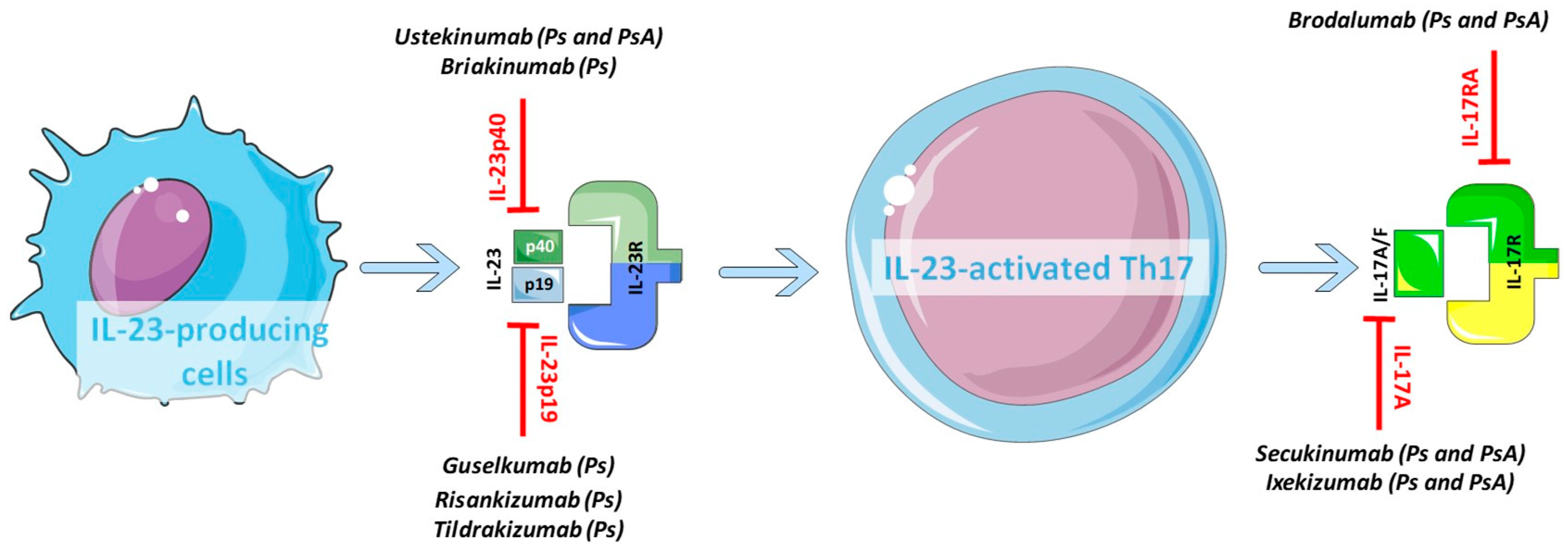


Ijms Free Full Text Role Of The Il 23 Il 17 Axis In Psoriasis And Psoriatic Arthritis The Clinical Importance Of Its Divergence In Skin And Joints Html



Jci The Il 23 Il 17 Axis In Inflammation
Interleukin (IL) 23/IL17 axis is a newly discovered proinflammatory signaling pathway and has been implicated in the pathogenesis of many chronic inflammatory and immune disorders Here we investigated whether the IL23/IL17 axis was present and functional in the lesions of oral lichen planus (OLP), a chronic inflammatory disease affecting the oral mucosaThis is a review of structural and functional data and the relationship to other closely related cytokines It provides an extensive review of historical data from animal models of autoimmunity and infectious disease concerning the IL12 axis and the relationship to new data regarding the IL23/Th17 axis 4••The role of IL23/IL17 axis in lupus nephritis Zhang Z(1), Kyttaris VC, Tsokos GC Author information (1)Division of Rheumatology, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA , USA T cells that express IL17 infiltrate the kidneys of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus


Jexpmed Although Many Inflammatory Diseases Share The Feature Of Elevated Il 17 Production Therapeutic Targeting Of Il 17 Has Vastly Different Clinical Outcomes This Review Summarizes Recent Progress In Understanding The Il 23 Il 17



The Role Of Il 17a In Axial Spondyloarthritis And Psoriatic Arthritis Recent Advances And Controversies Annals Of The Rheumatic Diseases
Interleukin23 (IL23) plays a pivotal role in stimulating the production of IL17 by activating the Th17 cells The IL23/IL17 axis is an important pathway for targeted therapy for inflammatory diseasesIL23/IL17 axis cytokines are important players in the pathogenesis of psoriasis and PsA Inhibition of IL23 and IL17 with MoAbs is a very effective therapy for both psoriasis and PsA The numbers of these agents are increasingThe IL23/IL17 immune axis seems especially important in CD, where it may function as a parallel pathway to the Th1 response coordinating inflammation1718 19 This work is a clinical



Highlighting Interleukin 36 Signalling In Plaque Psoriasis And Pustular Psoriasis Html Acta Dermato Venereologica



Pdf 9 The Il 23 Il 17 Immune Axis As A Promising New Target In The Treatment Of Spondyloarthritis Semantic Scholar
These new data suggest that the IL23/Th17 axis is a promising target for suppressing gut inflammation However, some important issues need to be clarified before moving to clinic For example, we do not yet know the exact role of each Th17 cytokine in the initiation and progression of gut inflammationThe IL23/IL17 axis plays an important role in the development of chronic inflammation and in host defenses against bacterial infection (A) In chronic inflammation, antigenstimulated dendritic cells and macrophages produce IL23, which promotes the development of Th17/Th IL17 cellsTravel reimbursements and honoraria from Novartis, Amgen and Janssen;



Interleukin 23 In The Skin Role In Psoriasis Pathogenesis And Selective Interleukin 23 Blockade As Treatment Abstract Europe Pmc



Figure 1 From Involvement Of The Il 23 Il 17 Axis And The Th17 Treg Balance In The Pathogenesis And Control Of Autoimmune Arthritis Semantic Scholar
Collectively, these studies indicate that the IL23IL17 axis participates in host defense against P carinii Pneumonia caused by Pneumocystis carinii remains an important cause of morbidity and mortality in the immunocompromised host (26, 27, 30)The IL23/IL17 axis in psoriatic arthritis @article{Suzuki14TheIA, title={The IL23/IL17 axis in psoriatic arthritis}, author={E Suzuki and E Mellins and M E Gershwin and F Nestle and I E Adamopoulos}, journal={Autoimmunity reviews}, year={14}, volume={13 45}, pages={ } }The IL23–IL17 immune axis from mechanisms to therapeutic testing Sarah L Gaffen 1, Renu Jain 2, Abhishek V Garg 1 & Daniel J Cua 2



Prostaglandin Mediates Il 23 Il 17 Induced Neutrophil Migration In Inflammation By Inhibiting Il 12 And Ifng Production Pnas



The Il 23 Il 17 Axis In Acute Tuberculosis 1 When Inflammatory Download Scientific Diagram
IL23/IL17 axis contributes to autoantibodydriven diseases B cells migrate between the dark and light zones of the germinal centers (GCs), a process mediated by CXCL12/CXCR4 and CXCL13/CXCR5The IL23–IL17 immune axis from mechanisms to therapeutic testing Sarah L Gaffen 1, Renu Jain 2, Abhishek V Garg 1 & Daniel J Cua 2The IL23/IL17 axis also plays a role in the symptoms development, as confirmed by the increased levels of IL17 and IL6 protein and mRNA in tears and saliva from SS patients compared to nonSS controls Additionally, the expression of Th17associated cytokines correlated with ocular surface parameters,


Stat3 Protein T Helper 17 Cell In Psoriasis By Yousry A Mawla


Update On Non Tnfi Therapies For Spondyloarthritis Ppt Video Online Download
OBJECTIVE The interleukin (IL)23/IL17 axis plays an important role in various inflammatory conditions but its function in acute pancreatitis (AP) is not well understood The present study investigated the relationship between serum levels of IL23, IL17, and Creactive protein (CRP) in patients and the severity of APThere is compelling evidence that interleukin (IL)23/IL17 axis plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of inflammatory spondyloarthritides including ankylosing spondylitis, reactive arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and inflammatory bowel diseaseassociated arthritis IL17 is a family of cytokines Of the six members of IL17, IL17A and IL17F are the most closely related proinflammatoryThe IL23/IL17 axis with PsA and the contribution of these master cytokines in the pathophysiology of the disease, highlighting the main cell types incriminated in PsA and



Il 23 Interleukin 23 Producing Conventional Dendritic Cells Control The Detrimental Il 17 Interleukin 17 Response In Stroke Stroke


Frontiers The Il 17 Family Of Cytokines In Psoriasis Il 17a And Beyond Immunology



Of Effects Of Il 23 Il 17 Immune Axis In Schizophrenia Download Scientific Diagram



A Cytokine Network Involving Il 36g Il 23 And Il 22 Promotes Antimicrobial Defense And Recovery From Intestinal Barrier Damage Pnas


Ijms Free Full Text Molecular Mechanisms And Management Of A Cutaneous Inflammatory Disorder Psoriasis Html



Ijms Free Full Text Role Of The Il 23 Il 17 Axis In Psoriasis And Psoriatic Arthritis The Clinical Importance Of Its Divergence In Skin And Joints Html



The Ifn G Il 12 Il 23 Il 17 Axis And Nadph Complex In Host Defense Download Scientific Diagram



Novel Pharmacological Approaches For Inflammatory Bowel Disease Targeting Key Intracellular Pathways And The Il 23 Il 17 Axis


Frontiers The Interleukin 23 Interleukin 17 Axis Links Adaptive And Innate Immunity In Psoriasis Immunology



Understanding The Il 23 Il 17 Immune Pathway Sciencedirect



Not Growth But Death Circulation Research


Therapeutic Potential Of Targeting Il 17 And Il 23 In Sepsis Clinical And Translational Medicine Full Text


Ijms Free Full Text Th17 Cells And The Il 23 Il 17 Axis In The Pathogenesis Of Periodontitis And Immune Mediated Inflammatory Diseases Html



Figure 6 Overexpression And Selectively Regulatory Roles Of Il 23 Il 17 Axis In The Lesions Of Oral Lichen Planus



Pdf The Il 23 Il 17 Axis In Psoriatic Arthritis Semantic Scholar



The Role Of Il 23 And The Il 23 Th17 Immune Axis In The Pathogenesis And Treatment Of Psoriasis Girolomoni 17 Journal Of The European Academy Of Dermatology And Venereology Wiley Online Library



Jci Insight Disrupting The Il 36 And Il 23 Il 17 Loop Underlies The Efficacy Of Calcipotriol And Corticosteroid Therapy For Psoriasis



Understanding The Il 23 Il 17 Immune Pathway Sciencedirect



Targeting The Il 17 Il 23 Axis In Chronic Inflammatory Immune Mediated Diseases Sciencedirect



Il 17 Signaling The Yin And The Yang Trends In Immunology



Pdf Il 17 Axis Disease Is Mediated Through The Il 23 In Experimental Inflammatory Bowel 2 E The Proinflammatory Effect Of Prostaglandin Semantic Scholar



Overexpression And Selectively Regulatory Roles Of Il 23 Il 17 Axis In The Lesions Of Oral Lichen Planus Topic Of Research Paper In Biological Sciences Download Scholarly Article Pdf And Read For Free On



Chronic Inflammation In Skin Malignancies



A Cytokine Network Involving Il 36g Il 23 And Il 22 Promotes Antimicrobial Defense And Recovery From Intestinal Barrier Damage Pnas



The Interleukin Il 23 Th17 Axis In The Immunopathogenesis Of Psoriasis Download Scientific Diagram



Involvement Of The Il 23 Il 17 Axis And The Th17 Treg Balance In The Pathogenesis And Control Of Autoimmune Arthritis Autoimmune Arthritis Autoimmune Arthritis
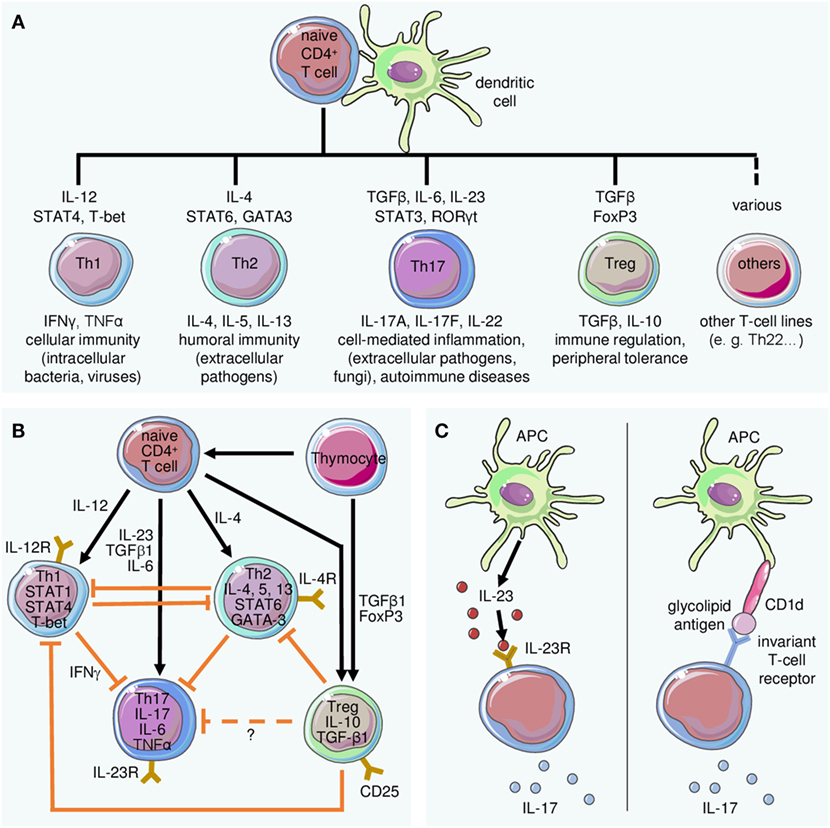


Frontiers The Interleukin 23 Interleukin 17 Axis Links Adaptive And Innate Immunity In Psoriasis Immunology



Novel Pharmacological Approaches For Inflammatory Bowel Disease Targeting Key Intracellular Pathways And The Il 23 Il 17 Axis



The Il 23 Th17 Axis In The Immunopathogenesis Of Psoriasis Sciencedirect
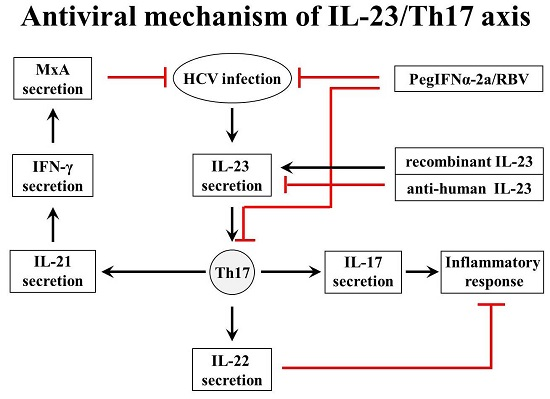


Ijms Free Full Text Involvement Of The Interleukin 23 Interleukin 17 Axis In Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection And Its Treatment Responses Html
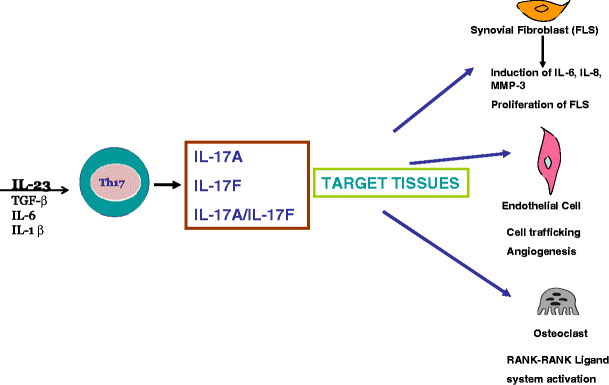


Il 23 Il 17 Axis In Spondyloarthritis Bench To Bedside Springerlink
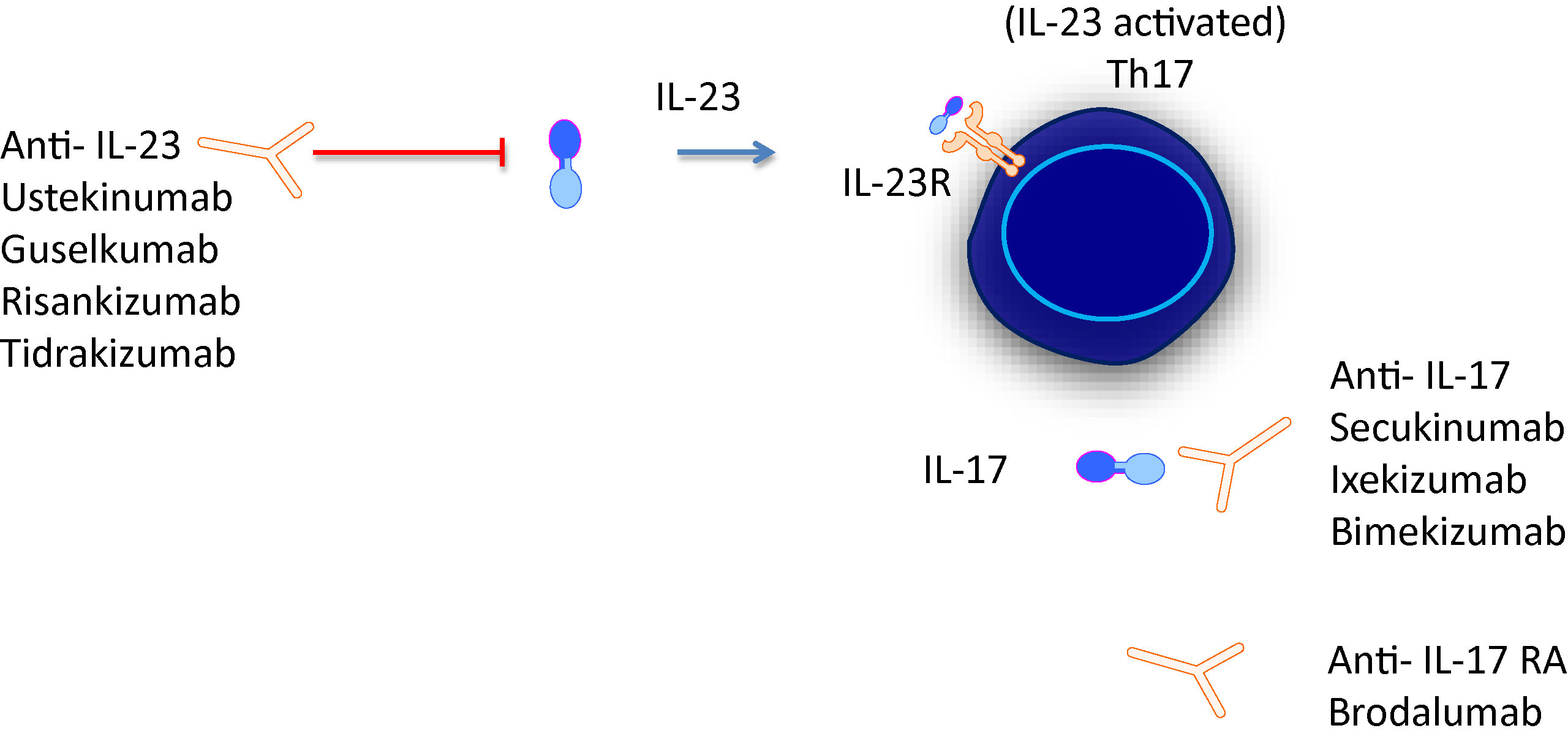


Frontiers Mini Review New Treatments In Psoriatic Arthritis Focus On The Il 23 17 Axis Pharmacology
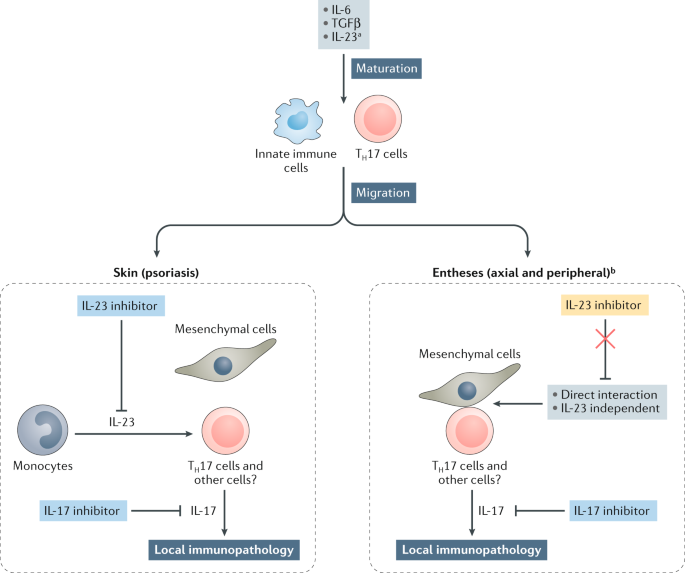


The Il 23 Il 17 Pathway As A Therapeutic Target In Axial Spondyloarthritis Nature Reviews Rheumatology



Oral Administration Of Vanillin Improves Imiquimod Induced Psoriatic Skin Inflammation In Mice Journal Of Agricultural And Food Chemistry X Mol
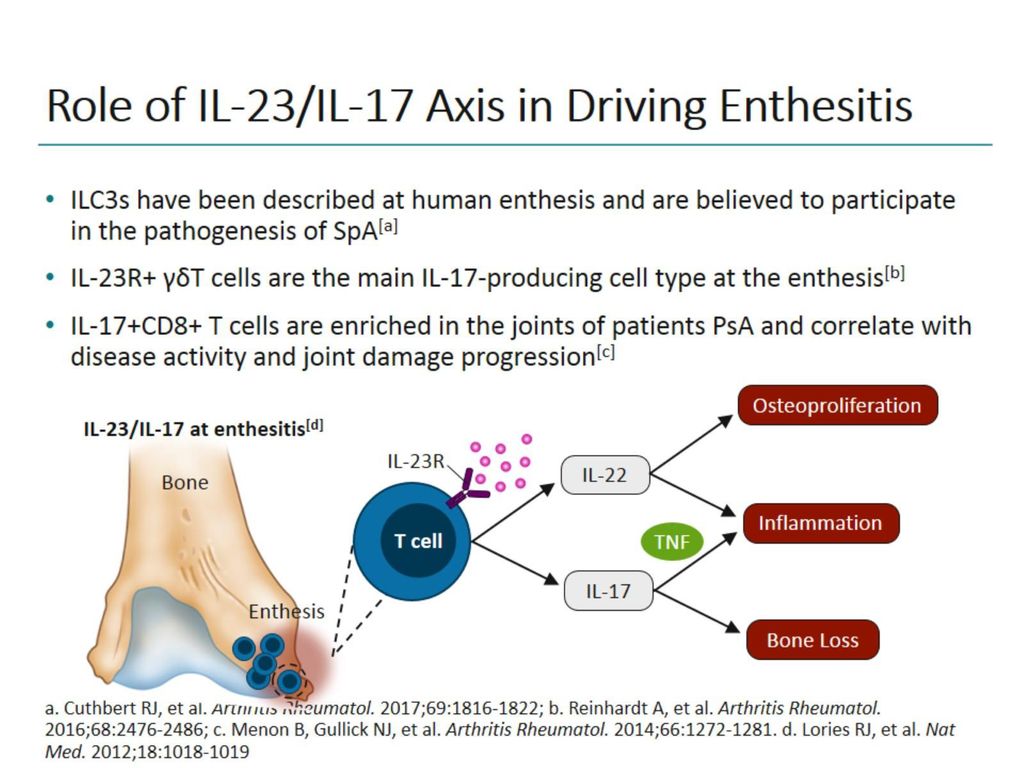


Il 12 And Il Ppt Download



Precarious Balance Th17 Cells In Host Defense Infection And Immunity
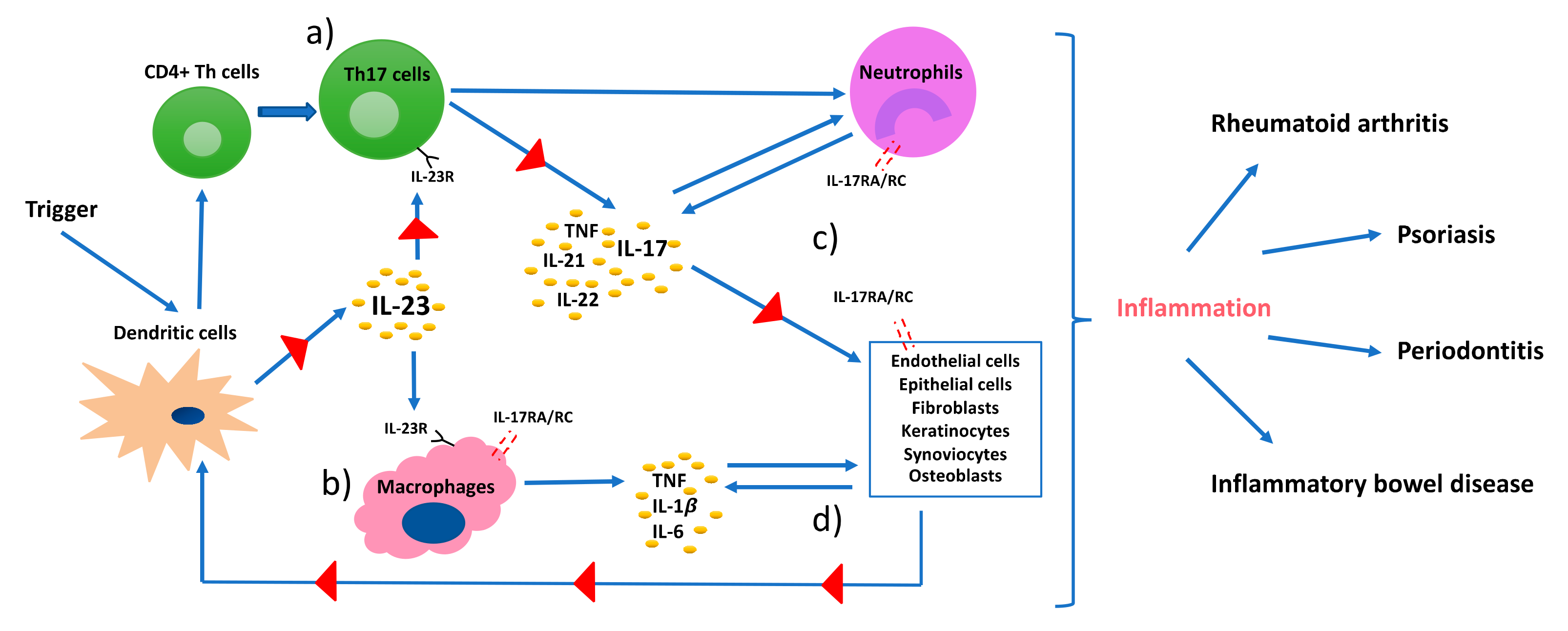


Ijms Free Full Text Th17 Cells And The Il 23 Il 17 Axis In The Pathogenesis Of Periodontitis And Immune Mediated Inflammatory Diseases Html



Il 36 Signaling Facilitates Activation Of The Nlrp3 Inflammasome And Il 23 Il 17 Axis In Renal Inflammation And Fibrosis American Society Of Nephrology


Plos Pathogens Hepatitis B Virus Induces Il 23 Production In Antigen Presenting Cells And Causes Liver Damage Via The Il 23 Il 17 Axis
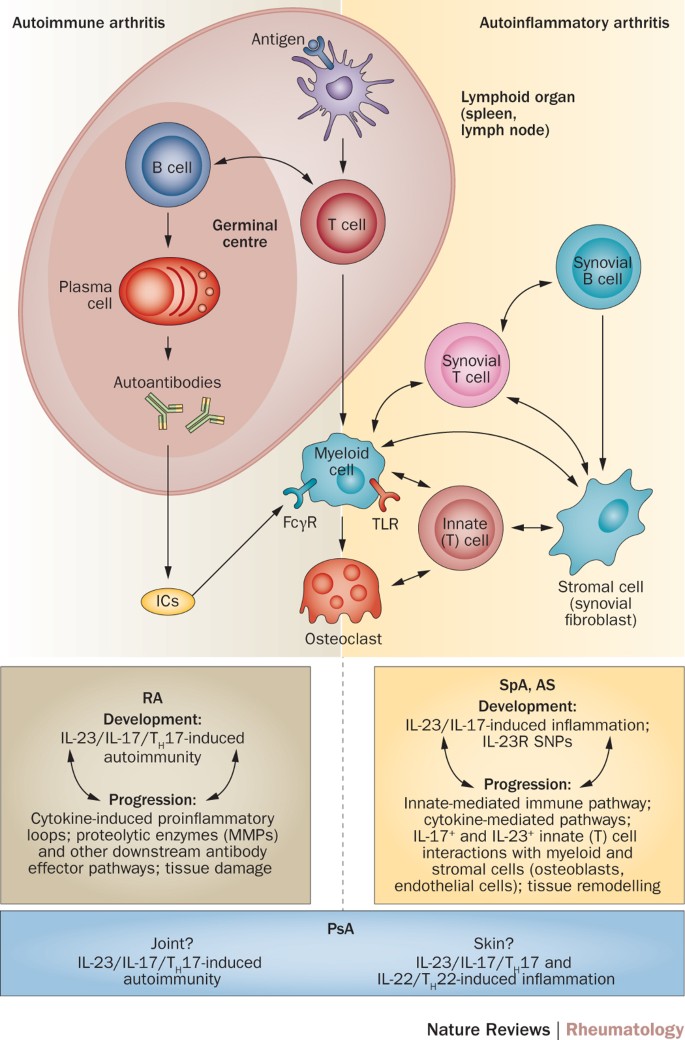


The Il 23 Il 17 Axis In Inflammatory Arthritis Nature Reviews Rheumatology



The Il 23 Il 17 Axis In Psoriatic Arthritis Sciencedirect


Plos One Faecalibacterium Prausnitzii Inhibits Interleukin 17 To Ameliorate Colorectal Colitis In Rats
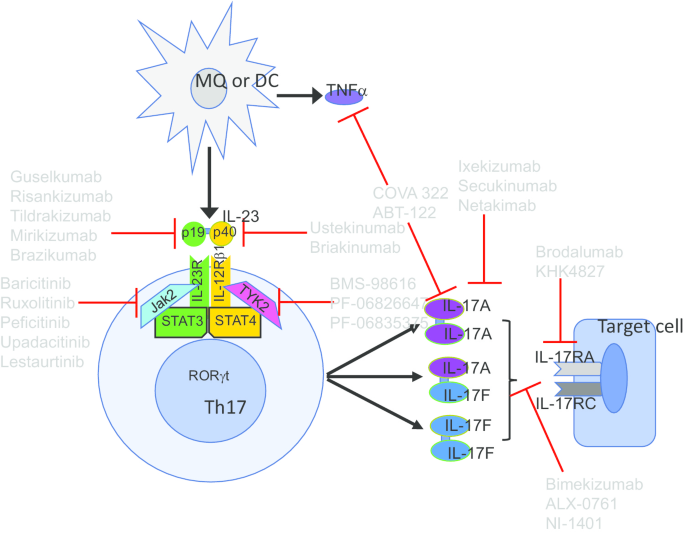


Il 23 Il 17 Axis In Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases Springerlink
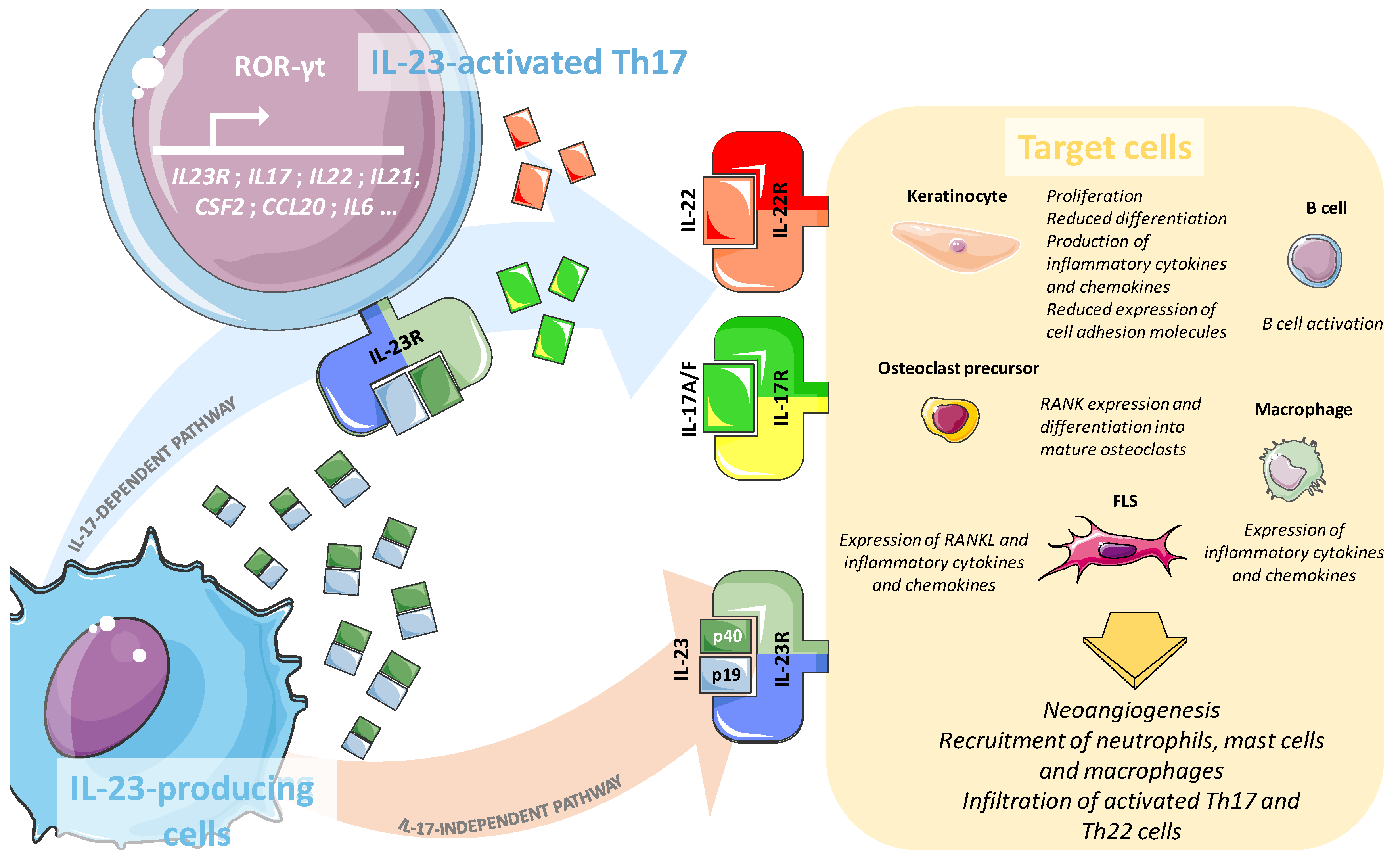


Ijms Free Full Text Role Of The Il 23 Il 17 Axis In Psoriasis And Psoriatic Arthritis The Clinical Importance Of Its Divergence In Skin And Joints Html



Interleukin 17 And Type 17 Helper T Cells Nejm



Schematics Of Il 23 Il 17 Immune Axis Involved In The Pathogenesis Of Download Scientific Diagram
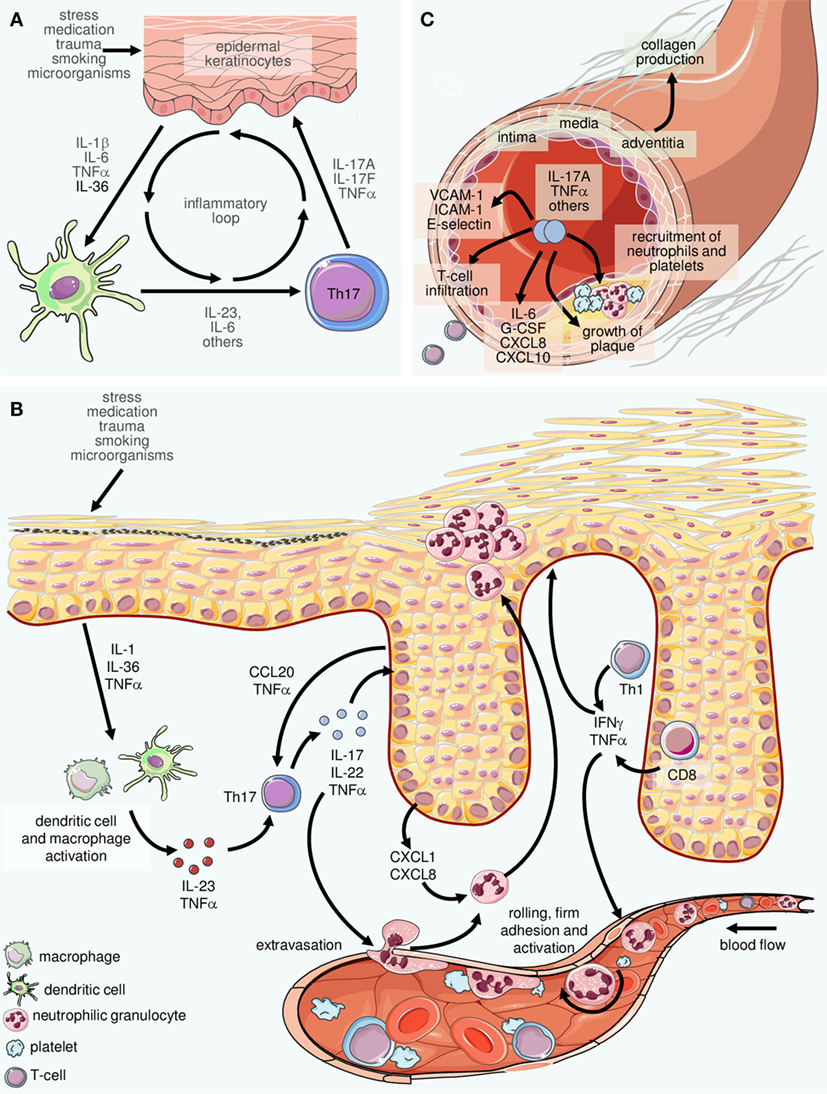


Frontiers The Interleukin 23 Interleukin 17 Axis Links Adaptive And Innate Immunity In Psoriasis Immunology


Th17 Cells Inflammation And Regulation



Top Pdf Il 17 1library
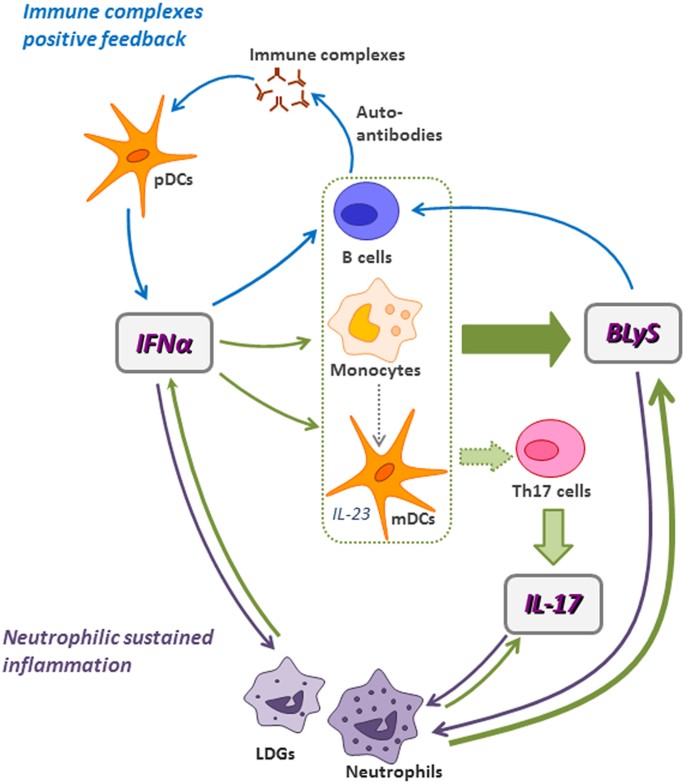


A Pathogenic Ifna Blys And Il 17 Axis In Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients Scientific Reports


Il 23 Signaling Regulation Of Pro Inflammatory T Cell Migration Uncovered By Phosphoproteomics



Jci The Il 23 Il 17 Axis In Inflammation



Pdf The Il 23 Th17 Axis In The Immunopathogenesis Of Psoriasis



The Th17 Il 23 Axis And Natural Immunity In Psoriatic Arthritis


Plos Pathogens Hepatitis B Virus Induces Il 23 Production In Antigen Presenting Cells And Causes Liver Damage Via The Il 23 Il 17 Axis
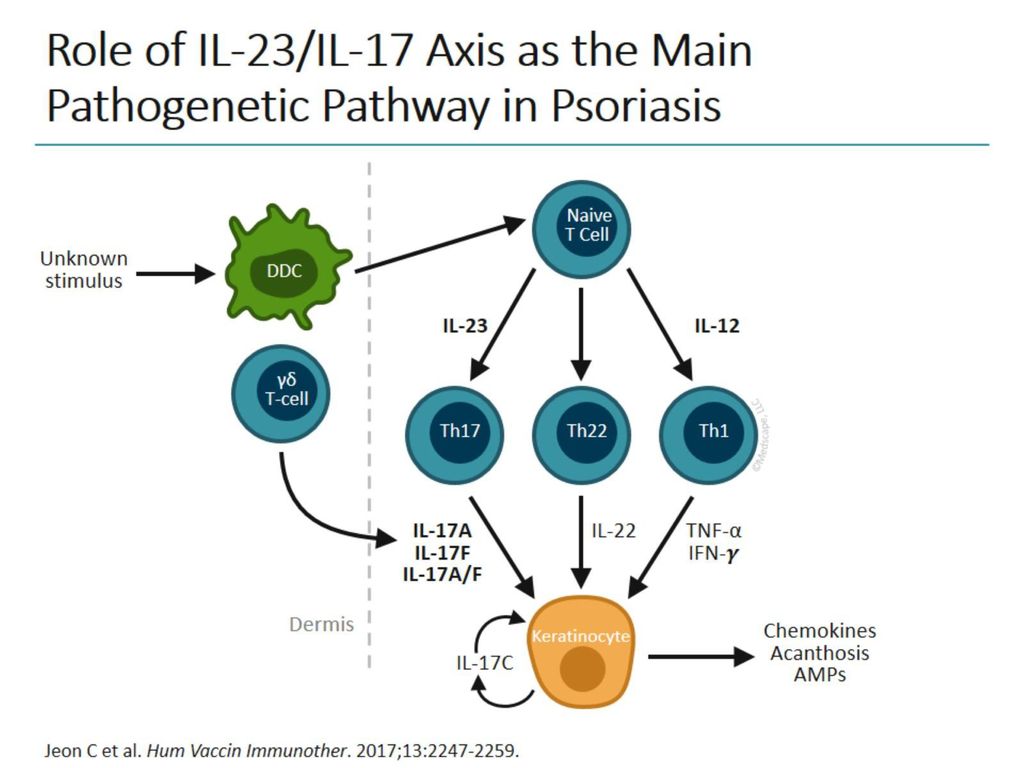


Evolution Of Treatment Strategies Targeting Il 23 For Psoriasis Ppt Download



Are Psoriasis And Psoriatic Arthritis The Same Disease The Il 23 Il 17 Axis Data Sciencedirect



Protumor Vs Antitumor Functions Of Il 17 The Journal Of Immunology
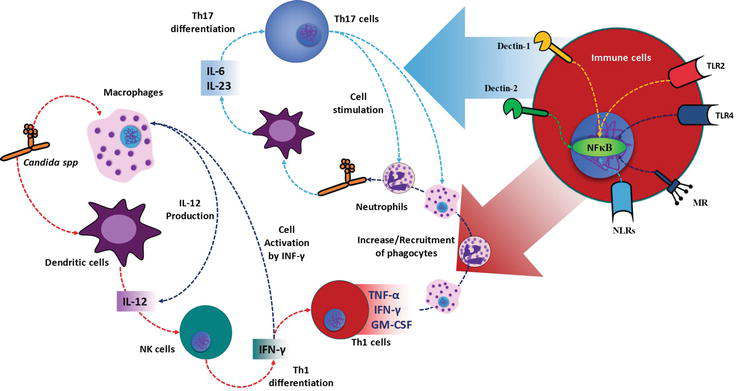


Cytokine Profiling Plays A Crucial Role In Activating Immune System To Clear Infectious Pathogens Intechopen
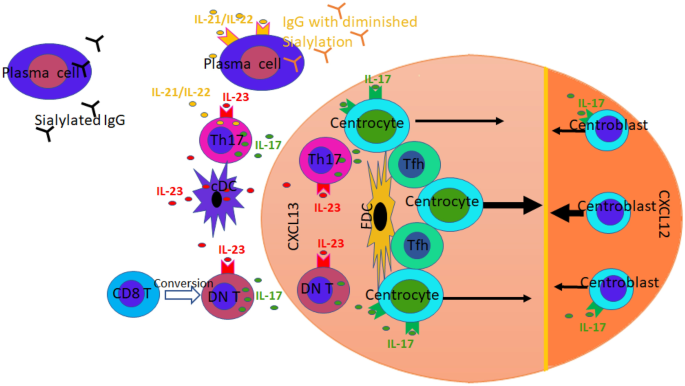


Il 23 Il 17 Axis In Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases Springerlink



Interleukin 17 Family Cytokines In Protective Immunity Against Infections Role Of Hematopoietic Cell Derived And Non Hematopoietic Cell Derived Interleukin 17s Matsuzaki 18 Microbiology And Immunology Wiley Online Library



Discovery Of The Il 23 Il 17 Signaling Pathway And The Treatment Of Psoriasis The Journal Of Immunology
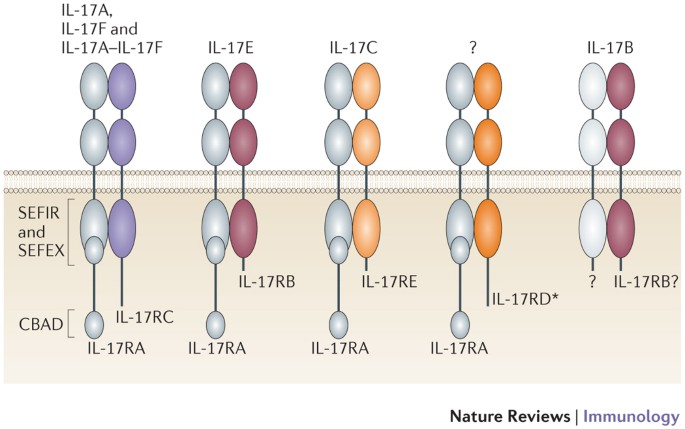


The Il 23 Il 17 Immune Axis From Mechanisms To Therapeutic Testing Nature Reviews Immunology
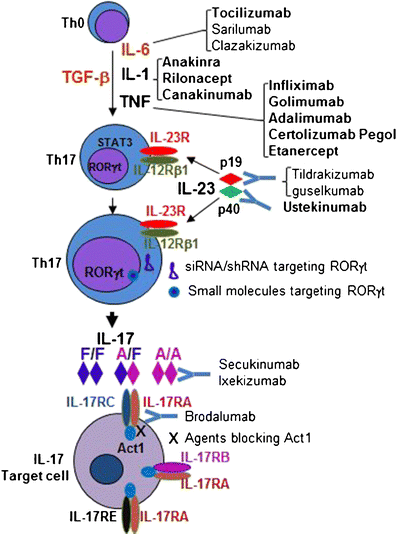


How Can We Manipulate The Il 23 Il 17 Axis Springerlink



The Cytokines Axis In Psoriasis Il 23 Il 17 Axis Related Mediators Download Scientific Diagram
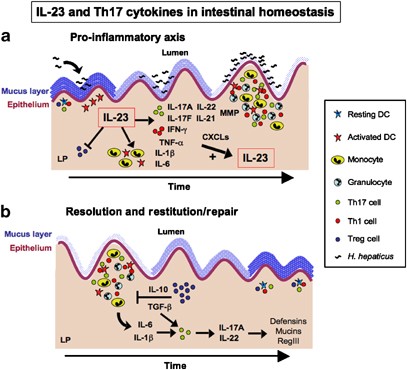


Il 23 And Th17 Cytokines In Intestinal Homeostasis Mucosal Immunology



Protumor Vs Antitumor Functions Of Il 17 The Journal Of Immunology



No comments:
Post a Comment